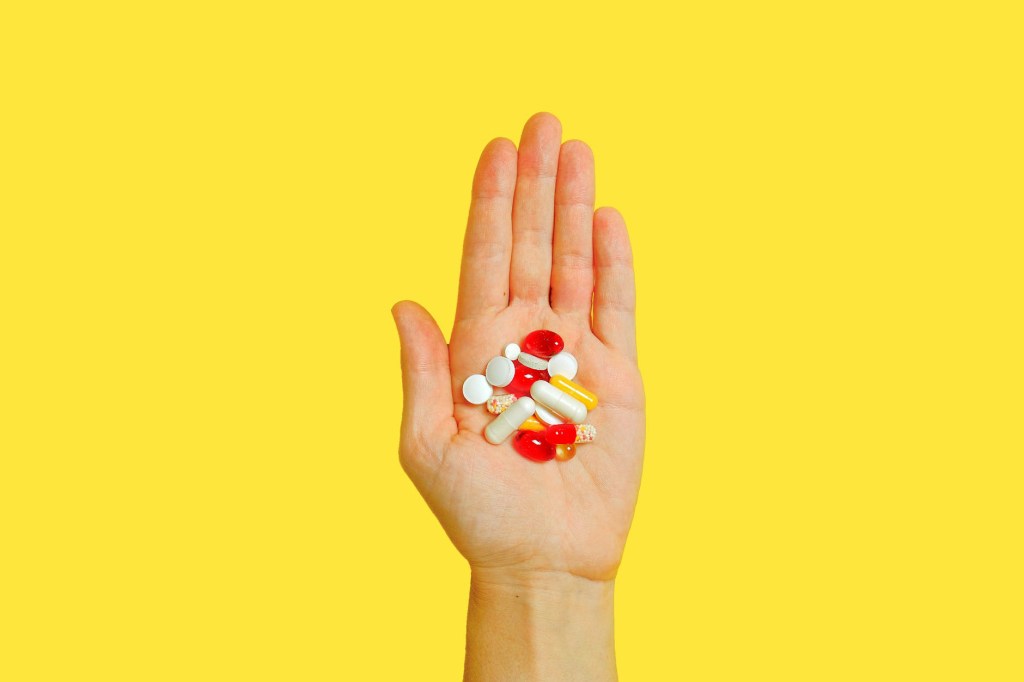
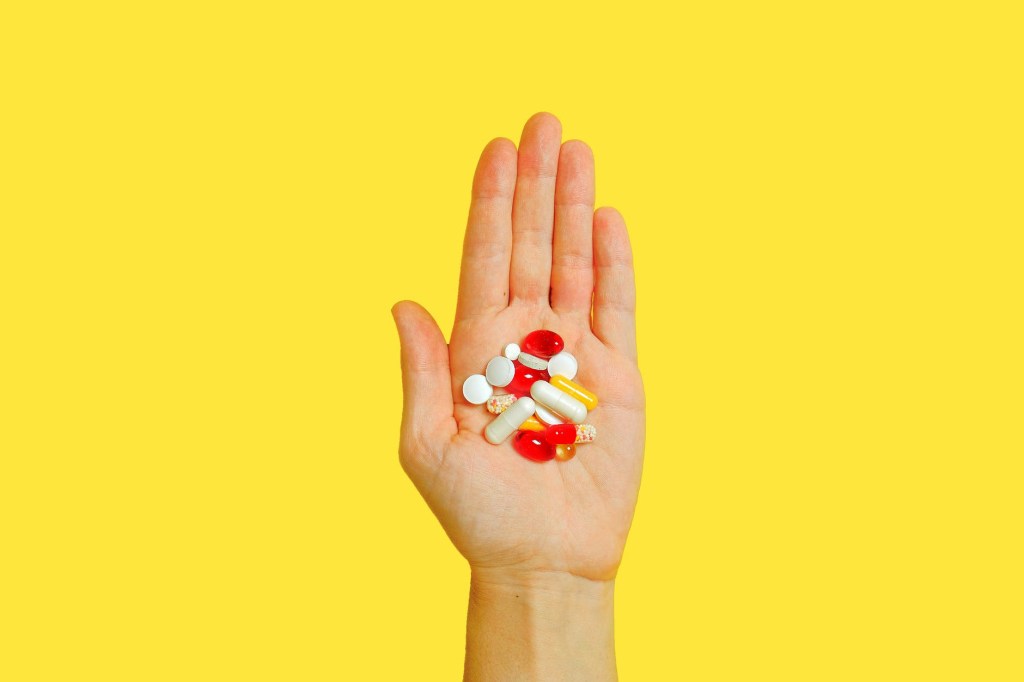
Absolutely Yes. Vitamins can cause harm.
Vitamins are very essential for life.
But too much of vitamins is bad.
You can buy paracetamol in a supermarket and it (rightly) comes with a big list of side effects .
You can freely buy various vitamins and supplements in supermarkets and none of them come with any warning what so ever.
Because vitamins are heavily promoted over Social media, newspapers, TV, and internet, many people think vitamins are safe and good. So people overindulge hoping for more benefits. But taking too much of vitamins is risky and can cause health problems due to Hypervitaminosis.
A recent article in Guardian points out the risks from taking too much of vitamin supplements. A man took too much of vitamin B6 and this resulted in damage to his nerves!
So be very careful with extra vitamins and supplements. Check whether you need the supplements at all. Try natural products rather than factory produced artificial supplements.
Reference
Guardian newspaper: Simon never linked the pain in his hands and feet to multivitamins – but a pathology test did. Natasha May and Sharlotte Thou. Published Sat 4 Jan 2025 19.00 GMT. Last modified on Sun 5 Jan 2025 01.55 GMT
Wiki. Hypervitaminosis

Disclaimer: Please note – This blog is NOT medical advice. This blog is NOT a expert medical opinion on various topics. This blog is purely for information research only and do check the sources where cited. Please DO consult your own doctor to discuss concerns and options, which are relevant and specific to you. The views expressed in this blog are NOT, in any way whatsoever, intended to be a substitute for professional advice.
The blog is NOT previewed, commissioned or otherwise endorsed, in any way, by any organisation that the author is associated with. The views expressed in this blog likely represents some of the author’s personal views held at the time of drafting the blog and MAY CHANGE overtime, particularly when new evidence comes to light.